This is a several part summary of the Udemy lesson: Blocchain and Bit coin fundamentals
- Part 1:
- Part 2
- Part 3
- Part 4
What is a Blockchain?
It is a constant growing ledger (a file) that helps a permanent record of all the transactions that have taken place in a:
- secured = it uses cryptography to lock the info inside the blockchain
- chronological,
- immutable way. The Ledger cannot be changed.`
Cryptograhic Hashing
Principle
Cryptographic hash is a digest/digital finger print of a certain amount of data. Hash is a 1 way function, i.e one can go from string to hash but cannot reconstruct string from hash. Encryption is different: you can reconstruct the string back from the encrypted value.
For example:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
import hashlib
m = hashlib.sha256()
s = "This is a transaction"
s_enc = s.encode("utf-8")
m.update(s_enc)
m.digest()
m.hexdigest()
72e4eafa97890f6c91c30ce9330c4112d688f40387679903f7bcbf69385d2520
SHA256 hash algo was developed by the NSA., where sha stands for secure hash algorithm.
Properties of hash functions:
-
Takes any string as input
-
fixed size output (256 bytes for bitcoin)
-
efficiently computable
Hash functions must be cryptographically secured:
- collision free:
The hash function must be collision free, i.e nobody can find a situation where:
It does not mean that the situation does not exist: it means that there is a very small probability of it occurring. If we assume collision-free hash, then:
- hiding property
We want something like this:
Given , it is infeasible to find . This is achieved with the following:
If is chosen from a probability distribution that has high min entropy (distribution is very spread out), then given ( and concatenated), it is infeasible to find .
- puzzle friendly
For every possible output value , if is chosen from a distribution with high min-entropy, then it is
infeasible to find such that . Puzzle friendly properties implies that no solving strategy is better than trying random values of . The puzzle friendly property implies that no solving strategy is better than trying random values of $x$.
Hash pointers and Data Structures
Hash Pointers
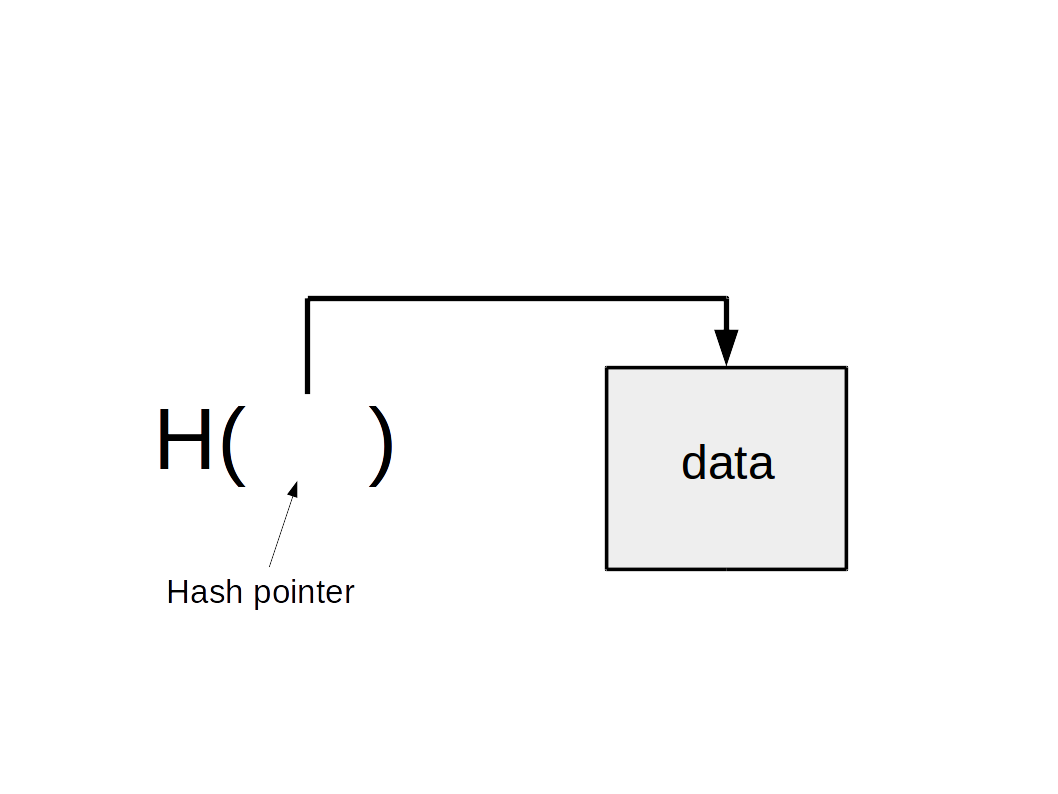
Hash pointer is:
-
pointer to where some info is stored, and
-
(cryptographic) hash of the info
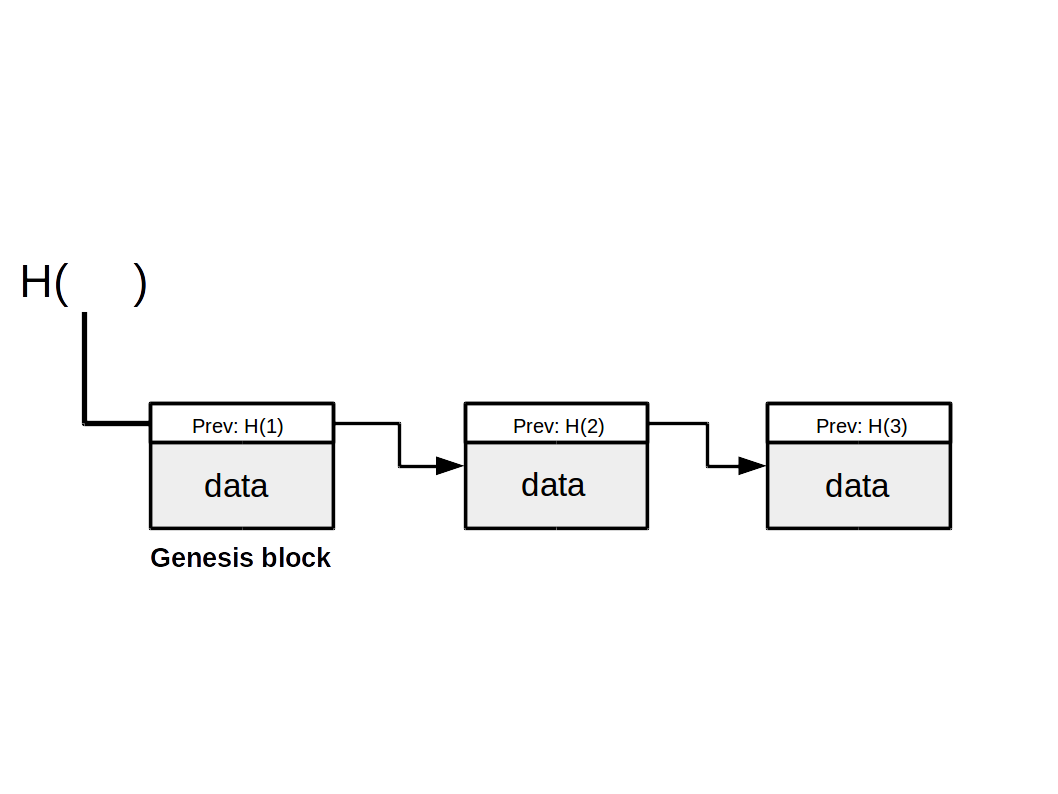
Hash pointers can be used to build data structures. For example:
Intro to Bitcoin
Build a block
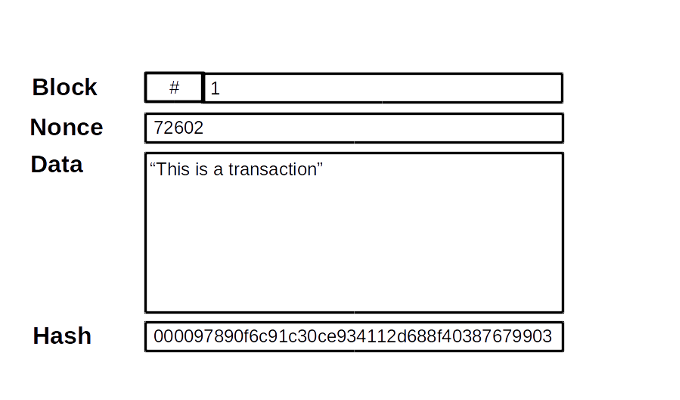
-
nounce: The nounce is a specific number when combined with the block number and the data, creates a hash with 4 leading
0000, and therefore make the block valid. -
hash: associated cryptographic hash. If the hash has 4 leading
0, it means that the block is valid. If changes are made to the data field, then the hash would not have 4 leading0, and the block will not be anymore valid.
Every block in a blockchain is cryptographically tighed to the next block.
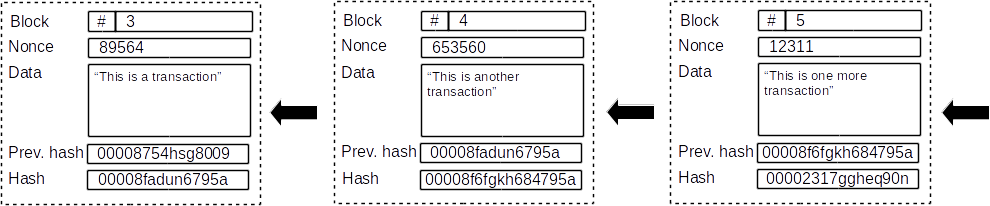
Any modification to a block, affect the following blocks, making the hash values of those blocks not valid.
Add transaction lives with other transactions happening in real time in something called the block. All transactions in the block must be validatedd, verified through mining.
Difficulty level
The 4 leading 0 are tied to the difficulty level. The difficulty level determines how difficult it
is to determine the cryptographic hash for a block. The difficulty level increases with time: the difficulty level is
adjusted every 2 weeks to make sure that the computer that are competing to solve this cryptographic problems
takes approximately 10 mins to mine a new block.
The computers are figuring out the required nonce to come up with a cryptgraphic hash that will be less than the
required target, i.e with the right number of leading 0s.
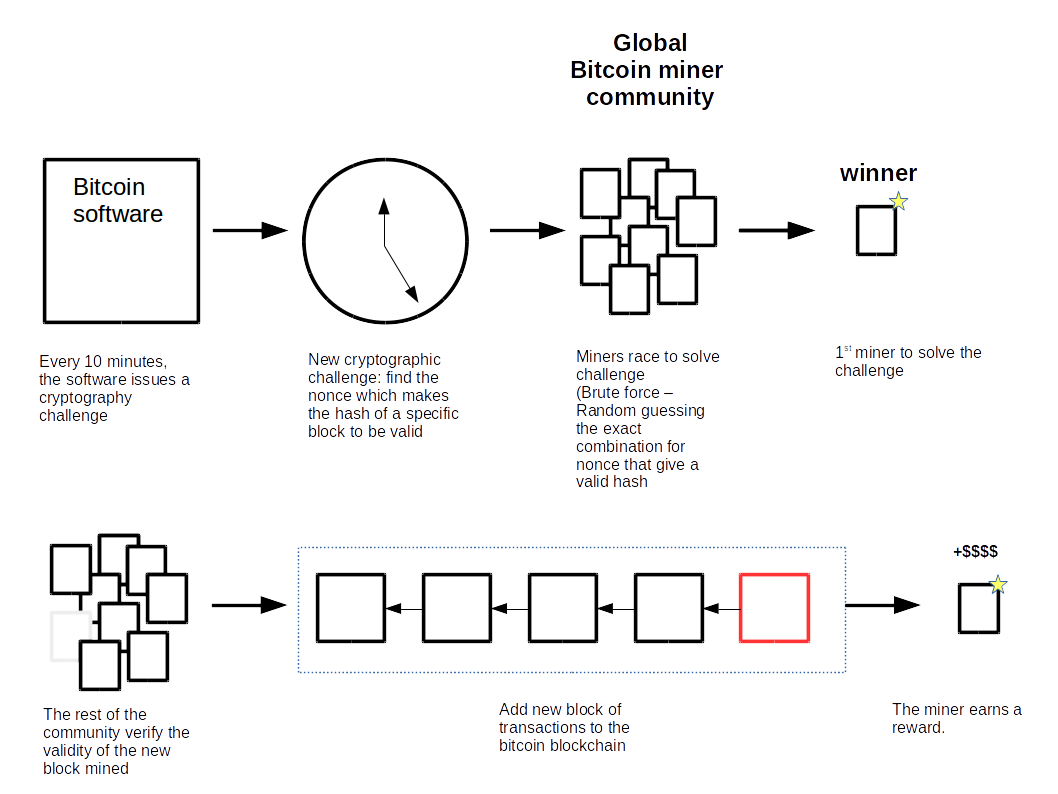
Miners
Mining consists in finding the nounce value using a computer. Miners process and confirm transactions by solving math challenge and resolving cryptography issues. For this task, miners are paid in bitcoin. Anyone can apply to be a miner. The role of the miner is to build the blockchain of records that form the bitcoin ledger. Mining is a reward system.
A new block is added every 10 minutes as new bitcoin transactions take place. The very first block (initial block) is the genesis block (Jan. 3rd 2009).
For a transaction to become confirmed, it needs to be successfully included in a block added by a minor onto the Bitcoin blockchain.
As part of creating a new block, the miners engage in a competition to be the fastest to find a block hash lower than a
required target number. This process involves hashing the block header data of the new block over and over with a different nonce,
until the sha256 hash that works is found.
Miners are paid for solving the block. This is the process by which new bitcoin are created.
The 4 components of Bitcoin
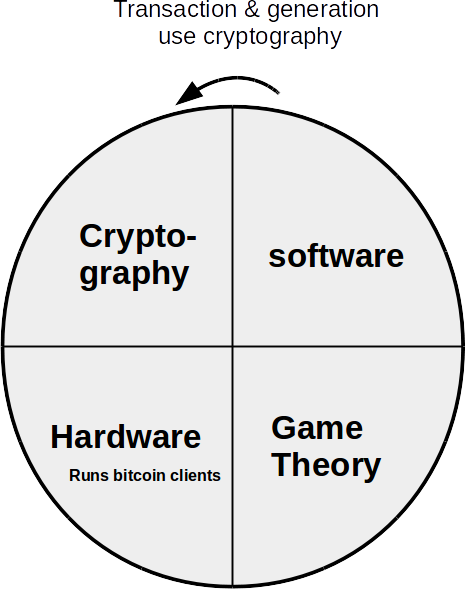
Consensus algorithms
Mining is part of the **proof of work consensus algorithm used in bitcoin to keep all the nodes in sync.
Consensus algorithms includes:
- proof of work: bitcoin
- proof of stake: does not require mining but uses validators
- WORKFLOW
Bit coin transfer of value
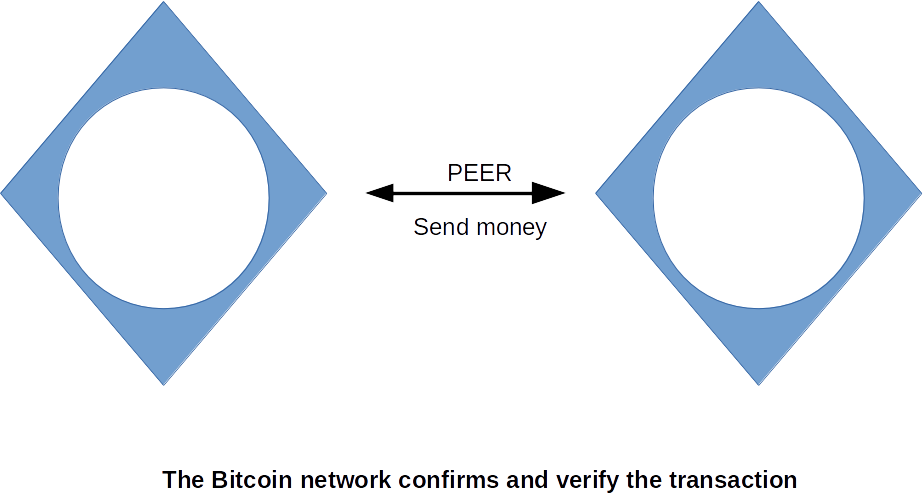
- Desintermediated: removes the middle man when transferring values/assets
- Distributed: the network runs a network of distributed computer
- Decentralized
Merkle Tree
Merkle Tree is a mathematical datastructure composed of hashes of different blocks of data, and which serves as a summary of all the transactions in the blocks.
Merkle root is a single cryptographic hash that serves as a summary of all the transactions.
Merkle Tree is a tree built of all the cryptographic hashes within the block
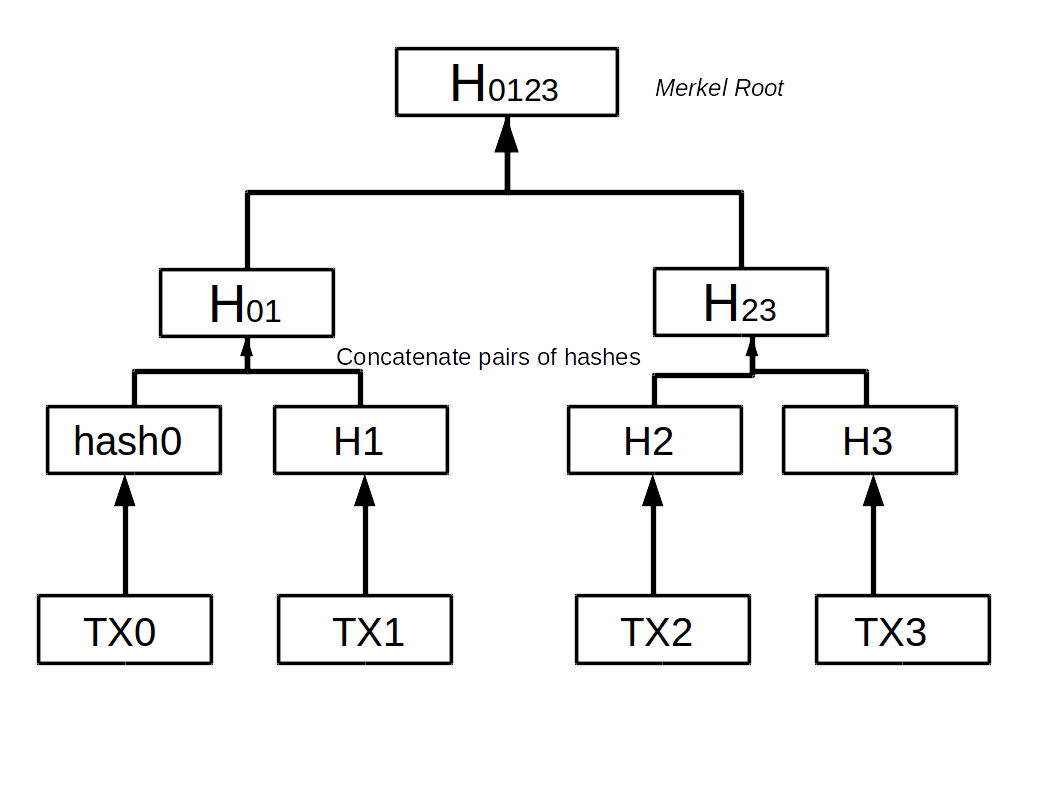
Any modification of the hashes below the Merkel Root will break other block below.
Vocabulary
-
FORK: a fork takes place when a blockchain splits into 2 different paths forward.
-
Hard Fork: introduces a change that forces everyone to upgrade
-
soft fork: introduces a change that is backwards compatible. No need to upgrade
FORKS on bitcoin happens on a regular basis: for example when 2 minors or more might solve a block at same time resulting in multiple forks. Eventually, one of the chains wins on the other: eventually the longer chain wins. The blocks that lost are called orphan blocks. The orphan blocks with the included transactions are pushed back into the Mempool waiting to be confirmed. They are not lost.
Gettign started Bitcoin
-
Install a wallet: a software to be installed on mobile device or computer which bitcoin.org for available wallet.
-
Get an address: you can have multiple address: 1 per transition
-
You receive a public key and a private key
Application of Blockchain
Blockchain Tokens
Token is an asset similarly to bitcoin.
IOT
IOT + blockchain for security issue
Blockchain technology for 2 devices to directly transfer a piece of property liek data between one another with a secured and reliable time stamped contractual handshake.
